
| Home | Web Design | Programming | Fairlight CMI | Soap Box | Downloads | Links | Biography | About... | Site Map |
 |
FAIRLIGHT CMI PAGE 4 |
| Fairlight CMI |
Examples | Swap Shop | Messageboard | Tales | Images | Wild | Technology | Voicetracker |
News Flash |
· GH Services is the North American distributor for BassLab of Germany.
Click here
for these unique guitars and basses. · Horizontal Productions repairs and upgrades Fairlight CMIs from Series I to MFX2. Visit http://www.horizontal.co.uk/. |
|
FAIRLIGHT CMI |
Page 4 is used to create voices through additive synthesis. The voices tend to have an "electronic" sound to them. |
|
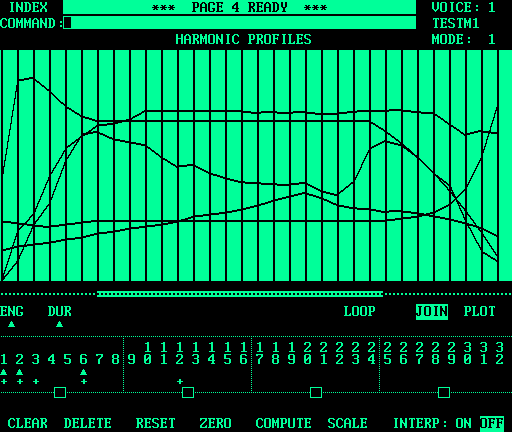
The preceding image shows a Mode 1 voice with several harmonic profiles. In effect, this is a "side view" which shows the harmonic amplitudes varying over time. Up to 32 harmonics can be controlled. A Mode 1 voice consists of 32 waveform segments, represented by the
vertical lines in the graph area. That gives 32 points per harmonic
profile. The length of time that each point sounds for is specified by a
duration profile ( The numbers across the bottom of the image show the status of the 32
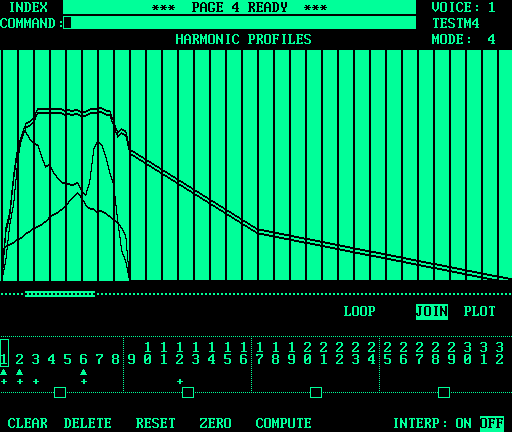
harmonics. A cross ( The Once harmonic amplitude profiles are drawn, the The The Mode 1 sounds are unique on the Fairlight CMI because they play for a fairly similar length of time, no matter the pitch. When a Mode 1 voice is played each segment is repeated a number of times, which is determined by a combination of the duration profile and the pitch. This is in contrast to sampled sounds and Mode 4 sounds, which become shorter as the pitch increases and the playback rate increases. The following image shows a Mode 4 voice. In fact, it is the previous Mode 1 voice converted to Mode 4, and then edited slightly. |
|
The harmonic profiles from the Mode 1 voice are compressed to the left-hand side in this image because a Mode 4 voice consists of 128 segments, in contrast to the 32 segments of a Mode 1 voice. Notice that even the loop has been visually compressed, but it will need to be re-established anyway as editing progresses. In a Mode 4 voice, the vertical divisions in the graph area represent every fourth segment. The 1st harmonic profile has been selected for editing. This is indicated with a double line on the graph and a box around the profile number. The Mode 4 voices use the entire 16,384 bytes of waveform memory, which is divided into 128 segments of 128 sample points each. Each segment contains one cycle (or period) of the waveform. Mode 1 voices only use the first 32 segments, or 4096 sample points total. If a Mode 1 voice were played at CD-quality speeds it would last less than 1/20th of a second! Although Page 4 is primarily used to create sounds with additive synthesis, it can also be used to alter sampled sounds. Sampling is usually performed into a Mode 4 voice, but if the voice is then converted into Mode 1, interesting results can be obtained. The energy and duration profiles have an effect on a converted sample,
but the individual harmonic profiles should be left empty during this
process. The energy and duration profiles take effect immediately, without
the need for executing the Some sampled voices sound rather robotic when converted into Mode 1. They have a kind of shimmering, quantized effect that is the result of stepping through the segments at a rate (determined by the duration profile) that is slower than normal. Sounds which are slower moving and less varying (such as choirs or string pads) sometimes respond well in Mode 1, because it extends the sample and makes the "throbbing" of the loop less prominent (or at least the same duration at every pitch). |
|
The following table summarizes the features of Mode 1 and Mode 4.
Previous page - Page 3: Keyboard Control |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home | Web Design | Programming | Fairlight CMI | Soap Box | Downloads | Links | Biography | About... | Site Map |
| Send comments about this site to Greg at
ghservices.com@gmail.com All trademarks contained herein are the property of their respective owners All pages copyright © 1996-2008 GH Services™ Created 1997-12-15 Last updated 2000-01-21 |